What are Data Structures?

According to Wikipedia,
In computer science, a data structure is a data organization and storage format that is usually
chosen for efficient access to data.More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data
values,
the relationships among them, and the functions or operations that can be applied to the data,
i.e.,
it is an algebraic structure about data.
In Simple words,
A data structure is a way to organize and store data so that it can be accessed and modified
efficiently.
In real world scenarios,
Think data structure as a bookshelf. You can store books in a bookshelf
in a particular order, retrieve them quickly, and add new books efficiently. Similarly, data
structures help in organizing and managing data effectively in software applications.
Data structures are fundamental in computer science, serving as the backbone for organizing and
processing data in various applications—from databases to machine learning algorithms.
Why Do We Need Data Structures?
What will happen if you store all your books in a single pile without any order? It will be hard to
find a specific book when you need it.

Caption: Organized vs. Unorganized Book Pile
Or think about students’ records in a school. If all the records are scattered randomly, it will be
challenging to retrieve a student’s information quickly.
Or think about how you look up a word in a dictionary. The words are arranged in alphabetical
order to make it easier to find the word you’re looking for. If the words were randomly placed, it
would be a nightmare to find anything.
Data structures help in organizing and managing data efficiently, making it easier to perform
operations like searching, sorting, and updating data. Here are some key reasons why data structures
Efficiency:
A well-chosen data structure allows for fast access and modification of data, making applications
run faster and more efficiently.Scalability:
The right data structure helps your application scale by ensuring that data can be managed
effectively, even when the amount of data grows.Optimization:
By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different data structures, you can optimize
algorithms to run with the least amount of time and memory.Maintainability:
Organized data structures make code easier to maintain. When data is structured logically,
updates or changes to the application become simpler and less error-prone.Readability:
A well-designed data structure improves the readability of your code by clearly defining how data
is stored and accessed. This makes it easier for other developers (or your future self) to
understand and work with the code.Reusability:
Efficient and well-implemented data structures can often be reused across different parts of a
program or even in entirely different projects, saving time and effort in the long run.Flexibility:
Data structures provide flexibility to handle different types of operations and adapt to specific
use cases. Whether you need fast lookups, ordered data, or dynamic resizing, there’s likely a
data structure that fits your needs.
With these benefits in mind, let’s explore how Kotlin offers unique tools to work with data
structures efficiently.
Data Structures in Kotlin
Kotlin, being a modern and expressive language, offers a rich set of built-in data structures. It is
interoperable with Java, which means you can also use Java’s collections and data structures in
Kotlin. However, Kotlin provides its own unique ways to handle data, often with more concise and
readable syntax.
Key Features of Kotlin Data Structures
Null Safety:
Kotlin’s null safety features reduce the risk of null pointer exceptions, making data handling
safer and more predictable.Immutable Collections:
Kotlin encourages the use of immutable collections, reducing bugs caused by accidental
modifications.Extension Functions:
Kotlin’s ability to extend existing types allows developers to enhance data structures with custom
functionality in a clean, readable manner.Concise Syntax:
Kotlin minimizes boilerplate code, allowing for simpler creation, access, and manipulation of data
structures.
This combination of features makes Kotlin an excellent choice for working with data structures,
whether you’re building a simple application or a complex algorithm.
Overview of Kotlin Data Structures
Kotlin provides a wide range of data structures to suit different needs. As Kotlin is interoperable
with Java, you can also use Java’s collections in Kotlin code. Here are some of the key data
structures available in Kotlin:
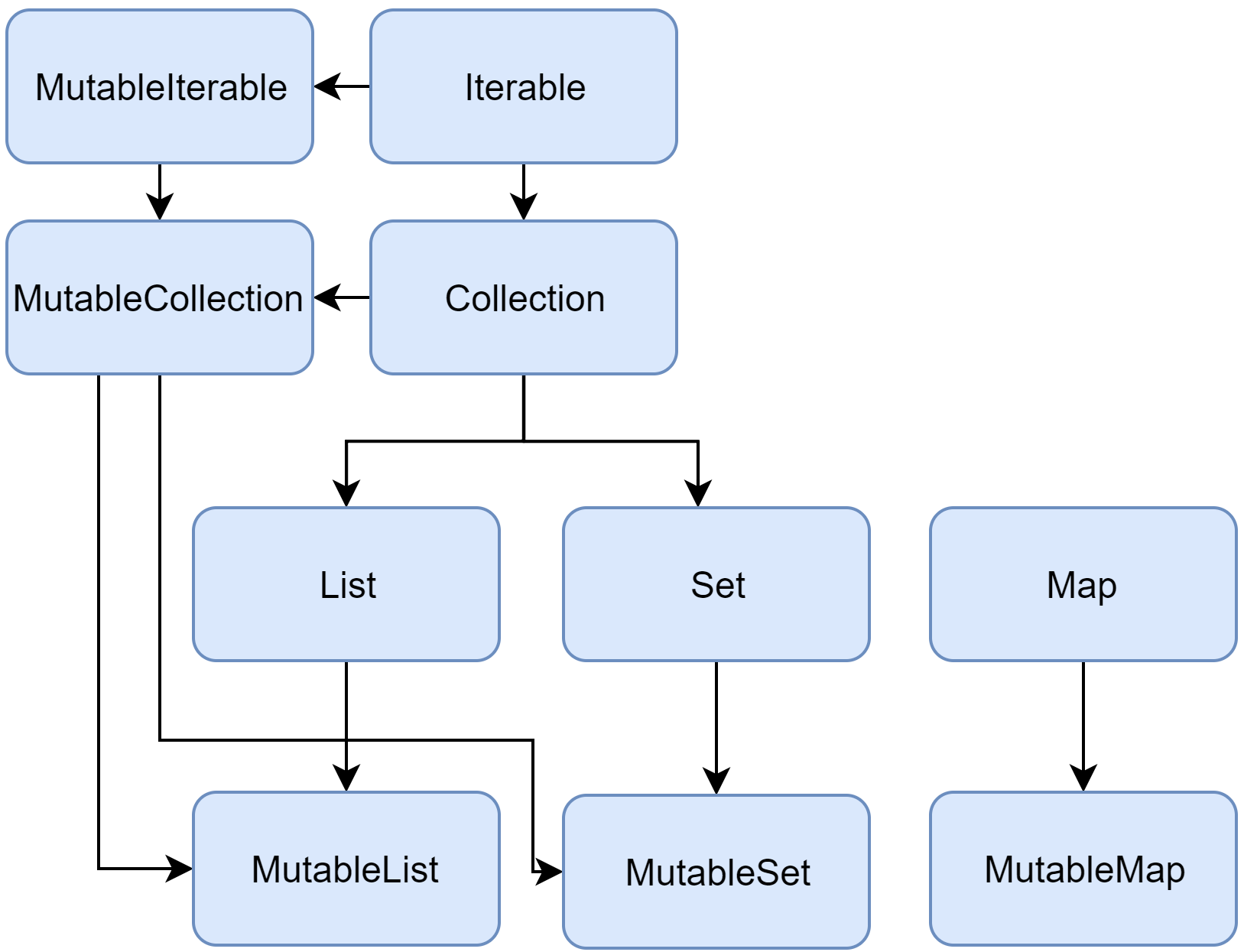
Caption: A diagram of the Kotlin collection interfaces
1. Array
- Array
:
A fixed-size array holding elements of typeT. It supports both read and write operations. - Specialized Arrays:
Optimized arrays for primitive types likeIntArray,CharArray, andByteArray, which offer
better performance than generic arrays.
2. List
- List
:
A read-only, ordered collection of elements that can contain duplicates. - MutableList
:
A modifiable version ofList, allowing addition, removal, and updating of elements.
3. Set
- Set
:
A collection of unique elements, ensuring no duplicates. - MutableSet
:
A mutable version ofSetthat supports modifications.
4. Map
- Map<K, V>:
A read-only collection of key-value pairs. Keys are unique, but values can repeat. - MutableMap<K, V>:
A modifiable version ofMapthat allows changes to keys and values.
5. Queue & Deque
- Queue
:
A collection following First-In-First-Out (FIFO) operations. Typically implemented usingArrayDequeorLinkedList. - ArrayDeque
:
A double-ended queue supporting fast operations from both ends. - LinkedList
:
A doubly linked list, also supportingQueueandDequeoperations.
6. Stack
- Stack
:
Follows Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) order. Can be implemented usingArrayDequeorMutableList.
7. Tree Structures
TreeMap<K, V>:
A map implementation that stores keys in sorted order.TreeSet
:
A set implementation that keeps elements sorted.(Note: TreeMap and TreeSet are accessible in Kotlin through Java interop.)
8. Pair & Triple
- Pair<A, B>:
Stores two related elements as a single object. - Triple<A, B, C>:
Stores three related elements.
These data structures provide a solid foundation for building efficient and scalable applications in
Kotlin.
Choosing the Right Data Structure
Understanding the available data structures and their use cases helps in selecting the best one for
your needs:
- Use Array for fixed-size, indexed data.
- Use List for ordered, dynamic data.
- Use Set to ensure uniqueness.
- Use Map for key-value relationships.
- Use Queue or Stack for specific ordering needs.
- Use TreeMap or TreeSet for sorted data (via Java interop).
By leveraging Kotlin’s concise and expressive syntax, you can work with these data structures
efficiently while taking advantage of features like null safety and immutability.
Conclusion
Data structures are the backbone of efficient programming, helping organize and process data
effectively. Kotlin, with its concise syntax, null safety, and rich standard library, offers a
modern approach to working with data structures. Whether you’re building simple applications or
solving complex problems, understanding the strengths and use cases of different data structures is
essential for writing clean, scalable, and maintainable code.
“Now that you’ve explored the basics of data structures in Kotlin, dive deeper into individual data
structures to understand their implementations and use cases. Check out the dedicated pages for a
step-by-step guide and code examples.
References
- Wikipedia - Data Structure
- Kotlin Collections
- Kotlin Standard Library
- Java Collections Framework
- Kotlin Data Structures